Abstract
Short Communication
Custom Implants and Beyond: The Biomedical Potential of Additive Manufacturing
Ashish Kumar Gupta*, Amit Choudhari, Abhishek Kumar and Anamika Gupta
Published: 17 May, 2024 | Volume 8 - Issue 2 | Pages: 050-055
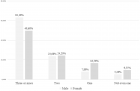
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is revolutionizing the field of biomedical engineering by enabling the creation of custom implants tailored to individual patient anatomy. This technology uses digital design files to layer-by-layer build structures from various materials, including biocompatible metals, polymers, and ceramics. In medical applications, this precision allows for the creation of implants that closely match the contours and geometries of a patient’s unique anatomical features, offering improved fit, functionality, and comfort compared to traditional, mass-produced implants. The potential benefits extend beyond just enhanced patient outcomes. With additive manufacturing, healthcare providers can reduce surgical times by designing implants that require minimal intraoperative modification. Moreover, the flexibility of this technology facilitates rapid prototyping and iterative design, enabling healthcare professionals to collaborate with engineers in refining implant designs before they are used in surgery. This iterative approach is particularly useful in complex cases, such as craniofacial reconstruction, where conventional implants may not adequately address the intricacies of a patient’s skeletal structure.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001094 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
References
- Ghomi ER, Khosravi F, Neisiany RE, Singh S, Ramakrishna S. Future of additive manufacturing in healthcare. Current Opinion in Biomedical Engineering. 2021; 17:100255; org/10.1016/j.cobme.2020.100255
- Choudhari A, Talkar S, Rayar P, Rane A. Design and manufacturing of compact and portable smart CNC machine. In: Vasudevan, H, Kottur, V, Raina, A (eds) Proceedings of International Conference on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering 2020: Springer; doi.org/101007/978-981-15-4485-9_21
- Griffiths L. CEIT Biomedical Engineering gets EU approval for 3D printed cranial implants [Internet]. TCTMAG. 18 November 2014. https://www.tctmagazine.com/additive-manufacturing-3d-printing-news/eu-approval-for-3d-printed-cranial-implants/.
- Ruban R, Rajashekhar VS, Nivedha B, Mohit H, Sanjay MR, Siengchin S. Role of additive manufacturing in biomedical engineering. Innovations in additive manufacturing: Springer. 2022; 139-57. doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89401-6_7
- Guzzi EA, Tibbitt MW. Additive Manufacturing of Precision Biomaterials. Adv Mater. 2020 Apr;32(13):e1901994. doi: 10.1002/adma.201901994. Epub 2019 Aug 18. PMID: 31423679.
- Datta A, Kumar A, Kumar A, Kumar A, Singh VP. Advanced materials in biological implants and surgical tools: CRC Press Boca Raton, FL, USA; 2022. eBook ISBN9781003344810
- Bai L, Gong C, Chen X, Sun Y, Zhang J, Cai L. Additive manufacturing of customized metallic orthopedic implants: Materials, structures, and surface modifications. Metals. 2019; 9(9):1004. doi.org/10.3390/met9091004
- Roy D, Chakraborty S, Gupta AK, Mallick AB, Koch CC. Synergistic effect of Nb and Zr addition in thermal stabilization of nano-crystalline Cu synthesized by ball milling. Materials Letters. 2020; 271:127780. doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127780
- Choudhari A, Rayar P, Shimpi S, Pawar N, Ambetkar S. Design and Development of Vacuum Frying Machine for the Production of High-Quality Fried Products. In: Vasudevan H, Kottur VKN, Raina AA, editors. Proceedings of International Conference on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation. Singapore: Springer; 2023. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Chapter 50. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7971-2_50
- Roy D, Chakraborty S, Gupta AK, BasuMallick A, Scattergood RO, Koch CC. Synergistic effect of Nb and Zr additions on the structure-property relationships of nanocrystalline Cu processed by mechanical alloying and hot pressing. Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 2021; 854:157174. doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157174
- Vignesh M, Ranjith Kumar G, Sathishkumar M, Manikandan M, Rajyalakshmi G, Ramanujam R. Development of biomedical implants through additive manufacturing: a review. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance. 2021; 30:4735-44. doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05578-7
- Wang Y, Tan Q, Pu F, Boone D, Zhang M. A review of the application of additive manufacturing in prosthetic and orthotic clinics from a biomechanical perspective. Engineering. 2020; 6(11):1258-66. doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2020.07.019
- Ramshaw JAM, Peng YY, Glattauer V, Werkmeister JA. Collagens as biomaterials. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009; 20(Suppl 1):3-8. doi: 10.1007/s10856-008-3415-4
- Gupta AK, Mallik B, Roy D. Structure Property Correlation of In Situ Reinforced Al–Based Metal Matrix Composite via Stir Casting. Mater Perform Charact. 2020; 9(1):25-35. doi: 10.1520/MPC20190038
- Jardini AL, Larosa MA, Macedo MF, Bernardes LF, Lambert CS, Zavaglia CAC. Improvement in cranioplasty: advanced prosthesis biomanufacturing. ProcediaCirp.2016; 49:203-8. doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2015.11.017
- Chen X, Possel JK, Wacongne C, van Ham AF, Klink PC, Roelfsema PR. 3D printing and modelling of customized implants and surgical guides for non-human primates. J Neurosci Methods. 2017 Jul 15;286:38-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2017.05.013. Epub 2017 May 13. PMID: 28512008; PMCID: PMC5482398.
- Phan K, Sgro A, Maharaj MM, D'Urso P, Mobbs RJ. Application of a 3D custom printed patient specific spinal implant for C1/2 arthrodesis. J Spine Surg. 2016 Dec;2(4):314-318. doi: 10.21037/jss.2016.12.06. PMID: 28097249; PMCID: PMC5233864.
- Dzian A, Živčák J, Penciak R, Hudák R. Implantation of a 3D-printed titanium sternum in a patient with a sternal tumor. World J Surg Oncol. 2018 Jan 15;16(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12957-018-1315-8. PMID: 29334989; PMCID: PMC5769524.
- Captiva Spine’s TirboLOX-L Titanium Lumbar Cages Receives FDA Clearance. https://spinalnewsinternational.com/captiva-spine-tirbolox/
- Wong KC, Kumta SM, Geel NV, Demol J. One-step reconstruction with a 3D-printed, biomechanically evaluated custom implant after complex pelvic tumor resection. Comput Aided Surg. 2015;20(1):14-23. doi: 10.3109/10929088.2015.1076039. Epub 2015 Aug 20. PMID: 26290317.
- Shuang F, Hu W, Shao Y, Li H, Zou H. Treatment of Intercondylar Humeral Fractures With 3D-Printed Osteosynthesis Plates. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jan;95(3):e2461. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002461. PMID: 26817880; PMCID: PMC4998254.
- Yazigi C, Chaar MS, Busch R, Kern M. The Effect of Sterilization on the Accuracy and Fit of 3D-Printed Surgical Guides. Materials (Basel). 2023 Jul 28;16(15):5305. doi: 10.3390/ma16155305. PMID: 37570008; PMCID: PMC10419648.
- Deswal H, Kapoor A, Sehgal K, Grover V. Use of Additive Manufacturing in Surgical Tools/Guides for Dental Implants. Additive Manufacturing with Medical Applications: CRC Press; 2022; 41-71. eBook ISBN9781003301066
- Singh M, Jonnalagadda S. Advances in bioprinting using additive manufacturing. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020 Feb 15;143:105167. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2019.105167. Epub 2019 Nov 26. PMID: 31778785.
- Mota C, Puppi D, Chiellini F, Chiellini E. Additive manufacturing techniques for the production of tissue engineering constructs. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015 Mar;9(3):174-90. doi: 10.1002/term.1635. Epub 2012 Nov 22. PMID: 23172792.
- Kumar R, Kumar M, Chohan JS. The role of additive manufacturing for biomedical applications: A critical review. Journal of Manufacturing Processes. 2021; 64:828-50. doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.02.022
- Kumar A, Datta A, Kumar A, Kumar A. Recent advancements and future trends in next-generation materials for biomedical applications. Advanced materials for biomedical applications: CRC Press; 2022; 1-19. eBook ISBN9781003344810
- Teo AJT, Mishra A, Park I, Kim YJ, Park WT, Yoon YJ. Polymeric biomaterials for medical implants and devices. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2016;2(4):454-472. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5b00429
- Talkar S, Choudhari A, Rayar P. Building envelope optimization and cost-effective approach in HVAC to support smart manufacturing. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation: ICIMA 2020. Springer Singapore; 2020. p. 299-308. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-4485-9_31
- Puppi D, Chiellini F. Biodegradable polymers for biomedical additive manufacturing. Applied materials today. 2020; 20:100700. doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100700
- Goffard R, Sforza T, Clarinval A, Dormal T, Boilet L, Hocquet S. Additive manufacturing of biocompatible ceramics. Adv Prod Eng Manag. 2013; 8:96-106. doi.org/10.14743/apem2013.2.157
- Bhargav A, Sanjairaj V, Rosa V, Feng LW, Fuh Yh J. Applications of additive manufacturing in dentistry: A review. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018 Jul;106(5):2058-2064. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33961. Epub 2017 Jul 24. PMID: 28736923.
- Buonamici F, Furferi R, Governi L, Lazzeri S, McGreevy KS, Servi M. A practical methodology for computer-aided design of custom 3D printable casts for wrist fractures. The Visual Computer. 2020; 36:375-90. doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-01624-z
- Azocar AF, Mooney LM, Duval JF, Simon AM, Hargrove LJ, Rouse EJ. Design and clinical implementation of an open-source bionic leg. Nat Biomed Eng. 2020;4(10):941-953. doi: 10.1038/s41551-020-00619-3
- Ku I, Lee GK, Park CY, Lee J, Jeong E. Clinical outcomes of a low-cost single-channel myoelectric-interface three-dimensional hand prosthesis. Arch Plast Surg. 2019 Jul;46(4):303-310. doi: 10.5999/aps.2018.01375. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Erratum in: Arch Plast Surg. 2019 Sep;46(5):491. PMID: 31336417; PMCID: PMC6657188.
- Martinez-Marquez D, Jokymaityte M, Mirnajafizadeh A, Carty CP, Lloyd D, Stewart RA. Development of 18 Quality Control Gates for Additive Manufacturing of Error Free Patient-Specific Implants. Materials (Basel). 2019 Sep 24;12(19):3110. doi: 10.3390/ma12193110. PMID: 31554254; PMCID: PMC6803939.
- Roy D, Gupta AK, Alam MS, Srikanth S, Jha BK. Enhancement of properties of micro-alloyed Low-carbon Ni-added Steel by thermomechanical treatment. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance. 2020; 29(12):7952-63. doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05311-w
- Culmone C, Smit G, Breedveld P. Additive manufacturing of medical instruments: A state-of-the-art review. Additive manufacturing. 2019; 27:461-73. doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.03.015
- Raheem AA, Hameed P, Whenish R, Elsen RS, G A, Jaiswal AK, Prashanth KG, Manivasagam G. A Review on Development of Bio-Inspired Implants Using 3D Printing. Biomimetics (Basel). 2021 Nov 19;6(4):65. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics6040065. PMID: 34842628; PMCID: PMC8628669.
Figures:
Similar Articles
-
Trichomonas Vaginalis-A Clinical ImageAstrit M Gashi*. Trichomonas Vaginalis-A Clinical Image. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hjcr.1001001; 1: 001-002
-
Gastric Mucosal CalcinosisVedat Goral*,Irem Ozover,Ilknur Turkmen. Gastric Mucosal Calcinosis. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hjcr.1001002; 1: 003-005
-
Giant Lipoma Anterior Neck: A case reportManu CB*,Gowri Sankar M,Arun Alexander. Giant Lipoma Anterior Neck: A case report . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hjcr.1001003; 1: 006-008
-
Catamenial pneumothorax: Presentation of an uncommon PathologyRui Haddad*,Caterin Arévalo,David Nigri. Catamenial pneumothorax: Presentation of an uncommon Pathology . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hjcr.1001004; 1: 009-013
-
A rare case: Congenital Megalourethra in prune belly syndromeNuman Baydilli*,Ismail Selvi,Emre Can Akınsal. A rare case: Congenital Megalourethra in prune belly syndrome. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001005; 2: 001-003
-
Trauma to the neck: Manifestation of injuries outside the original zone of injury-A case reportStephen O Heard*,Alexander Christakis,Brian Tashjian,Anne M Gilroy3. Trauma to the neck: Manifestation of injuries outside the original zone of injury-A case report. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001006; 2: 004-009
-
Meige Trofoedema: A form of primary lymphedemaCarlos Al Sanchez Salguero*. Meige Trofoedema: A form of primary lymphedema. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001007; 2: 010-014
-
A rare case of Diabetic Foot in male of middle age has been shown Diabetic footSujit K Bhattacharya*. A rare case of Diabetic Foot in male of middle age has been shown Diabetic foot. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001008; 2: 015-015
-
Brooke-Spiegler Syndrome: A rare cause of skin appendageal tumorN Suganthan*,S Pirasath,DD Dikowita. Brooke-Spiegler Syndrome: A rare cause of skin appendageal tumor. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001009; 2: 016-018
-
McArdle’s Disease (Glycogen Storage Disease type V): A Clinical CaseCameselle-Teijeiro JF*,Calheiros-Cruz T,Caamaño-Vara MP,Villar-Fernández B,Ruibal-Azevedo J,Cameselle-Cortizo L,Cameselle-Arias M,Charro Gamallo ME,Turienzo-Pacho F,Yera Acosta A. McArdle’s Disease (Glycogen Storage Disease type V): A Clinical Case. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001010; 2: 019-023
Recently Viewed
-
Synthesis of Carbon Nano Fiber from Organic Waste and Activation of its Surface AreaHimanshu Narayan*,Brijesh Gaud,Amrita Singh,Sandesh Jaybhaye. Synthesis of Carbon Nano Fiber from Organic Waste and Activation of its Surface Area. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2019: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001017; 2: 056-059
-
Obesity Surgery in SpainAniceto Baltasar*. Obesity Surgery in Spain. New Insights Obes Gene Beyond. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.niogb.1001013; 4: 013-021
-
Tamsulosin and Dementia in old age: Is there any relationship?Irami Araújo-Filho*,Rebecca Renata Lapenda do Monte,Karina de Andrade Vidal Costa,Amália Cinthia Meneses Rêgo. Tamsulosin and Dementia in old age: Is there any relationship?. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2019: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001025; 3: 145-147
-
Case Report: Intussusception in an Infant with Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection and Post-Operative Wound DehiscenceLamin Makalo*,Orlianys Ruiz Perez,Benjamin Martin,Cherno S Jallow,Momodou Lamin Jobarteh,Alagie Baldeh,Abdul Malik Fye,Fatoumatta Jitteh,Isatou Bah. Case Report: Intussusception in an Infant with Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection and Post-Operative Wound Dehiscence. J Community Med Health Solut. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmhs.1001051; 6: 001-004
-
The prevalence and risk factors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetes mellitus follow-up patients at Debre Berhan Referral Hospital, Central EthiopiaGetaneh Baye Mulu,Worku Misganew Kebede,Fetene Nigussie Tarekegn,Abayneh Shewangzaw Engida,Migbaru Endawoke Tiruye,Mulat Mossie Menalu,Yalew Mossie,Wubshet Teshome,Bantalem Tilaye Atinafu*. The prevalence and risk factors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetes mellitus follow-up patients at Debre Berhan Referral Hospital, Central Ethiopia. J Clini Nephrol. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001104; 7: 025-031
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."